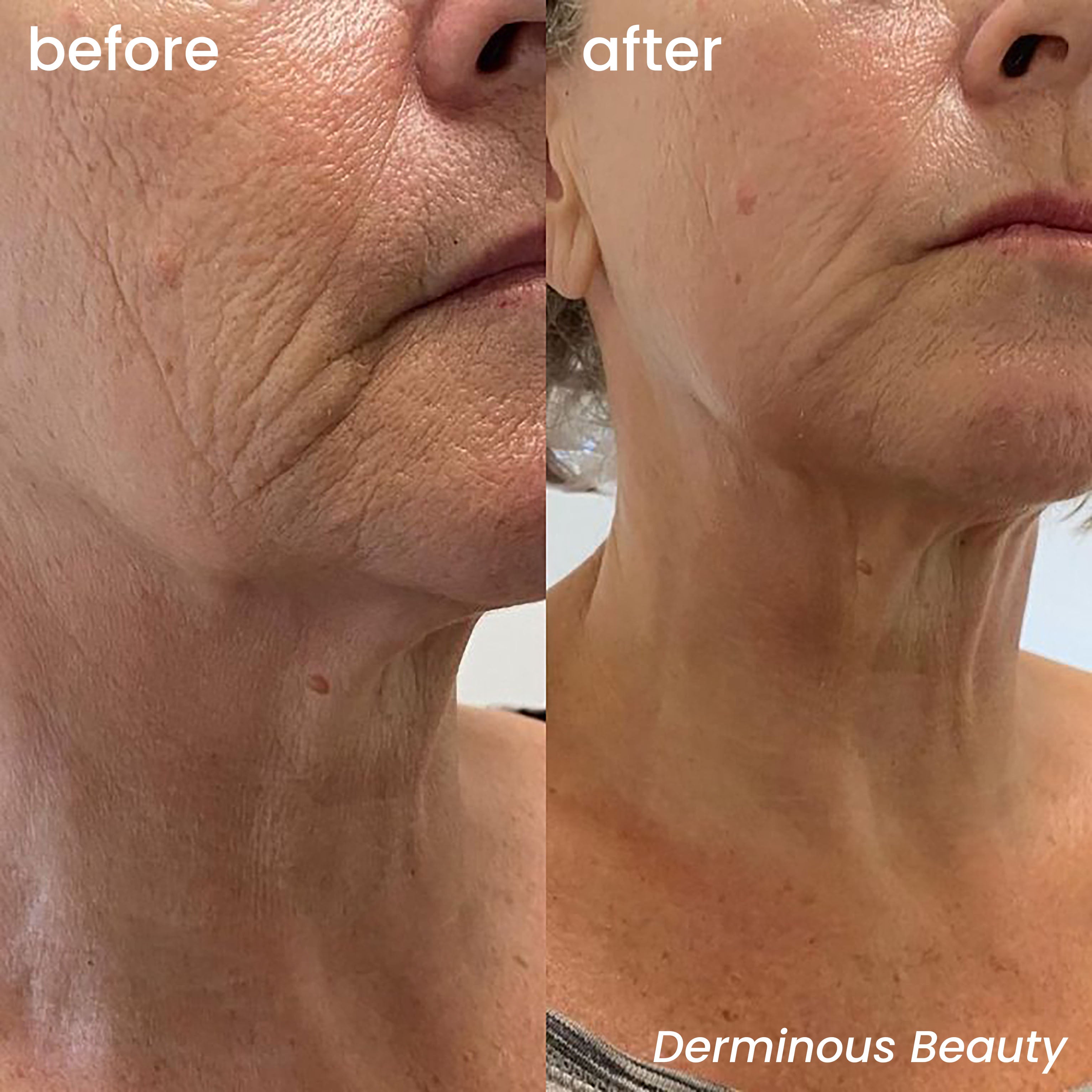
Brightening Your Complexion with Niacinamide and Vitamin C
In the ever-evolving world of skincare, achieving a radiant, even-toned complexion remains a top priority for consumers worldwide. Two powerhouse ingredients—niacinamide and vitamin C—have emerged as cornerstones of brightening regimens, celebrated not only for their efficacy but also for their compatibility with diverse skin types, including sensitive and post-procedure skin. When combined intelligently, these actives work synergistically to tackle hyperpigmentation, dullness, inflammation, and signs of aging. This article explores the science behind niacinamide and vitamin C, debunks common myths, and introduces an innovative at-home clinical-grade system—Derminous GeneLift™—that leverages both ingredients within a precision micro-infusion framework to deliver visible, transformative results.
The Science Behind Niacinamide: More Than Just Brightening
Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide, is a water-soluble form of vitamin B3. Unlike its precursor niacin (which can cause flushing), niacinamide is exceptionally well-tolerated and boasts a robust portfolio of dermatological benefits. Clinical studies have demonstrated its ability to inhibit melanosome transfer from melanocytes to keratinocytes, effectively reducing the appearance of dark spots and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation[1] . Additionally, niacinamide strengthens the skin barrier by boosting ceramide synthesis, enhances hydration via increased natural moisturizing factors (NMFs), and exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that benefit acne-prone and rosacea-affected skin[2] .


Notably, Derminous incorporates a patented niacinamide formulation (Patent No. ZL 2020116206743) that precisely controls residual nicotinic acid content—a common irritant in lower-grade niacinamide products—ensuring maximum brightening with minimal sensitivity[3] . This innovation aligns with the brand’s core value of “precision and purity,” making it ideal for post-microneedling or compromised skin states.

Vitamin C: The Gold Standard Antioxidant (and Why It’s Not in Every Formula)
Vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid) is widely regarded as the gold-standard topical antioxidant. It neutralizes free radicals generated by UV exposure and pollution, stimulates collagen synthesis, and directly inhibits tyrosinase—the key enzyme in melanin production—thus lightening existing pigmentation[4] . However, pure L-ascorbic acid is notoriously unstable; it oxidizes rapidly when exposed to light or air, turning yellow or brown and losing efficacy.






Interestingly, Derminous GeneLift™ does not list L-ascorbic acid among its primary ingredients. Instead, it employs tranexamic acid (also known as TXA or "凝血酸" in Chinese formulations)—a molecule increasingly recognized as a gentler, more stable alternative for brightening, especially in sensitive or post-procedure skin. Tranexamic acid works by interfering with the plasminogen/plasmin pathway in keratinocytes, which indirectly suppresses UV-induced melanin production without the irritation risks associated with high-concentration vitamin C[5] .

This strategic choice reflects Derminous’ commitment to clinical safety and barrier respect—a philosophy that prioritizes long-term skin health over aggressive, short-term results. For users seeking vitamin C-like brightening without instability or stinging, tranexamic acid offers a compelling solution, particularly when delivered via enhanced penetration methods like microneedling.
Synergy Through Delivery: Why Topical Application Isn’t Enough
Even the most potent actives fail if they cannot penetrate the stratum corneum—the skin’s outermost barrier. Traditional serums often deliver less than 10% of active ingredients into viable epidermal layers[6] . This is where micro-infusion technology becomes transformative.
Derminous GeneLift™ utilizes a 24K gold-plated micro-infusion device made of medical-grade stainless steel. The ultra-fine needles (typically 0.2–0.3mm in length) create transient microchannels that bypass the barrier, allowing high-molecular-weight actives like PDRN (Polydeoxyribonucleotide), soluble collagen, and multi-peptides to reach deeper dermal layers where they exert regenerative effects[7] .
Crucially, gold’s natural anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties reduce redness and infection risk—making this system uniquely suitable for sensitive or reactive skin. In fact, clinical data shows that microneedling can increase transdermal absorption by up to 300%, turning otherwise superficial treatments into truly bioactive interventions[8] .
When niacinamide and tranexamic acid are delivered via this method—as in the GeneLift™ serum—they achieve concentrations in the epidermis and upper dermis that would be impossible with passive application alone. The result? Faster, more pronounced brightening, reduced pore appearance, and improved texture within just 2–4 weeks of biweekly use.
Beyond Brightening: A Holistic Anti-Aging Ritual
Derminous frames its system not merely as a treatment but as a “ritual of transformation.” The four-step protocol—Activate, Infuse, Soothe, Seal—mirrors professional medspa protocols:
- Micro-Infusion Activation: 24K gold needles open pathways.
- Precision Infusion: Serum rich in niacinamide, PDRN, Syn-Ake (a synthetic snake venom peptide), and DNA sodium delivers multi-targeted correction.
- Post-Treatment Repair Mask: Formulated with recombinant fibronectin, panthenol, and allantoin to calm inflammation and accelerate barrier recovery.
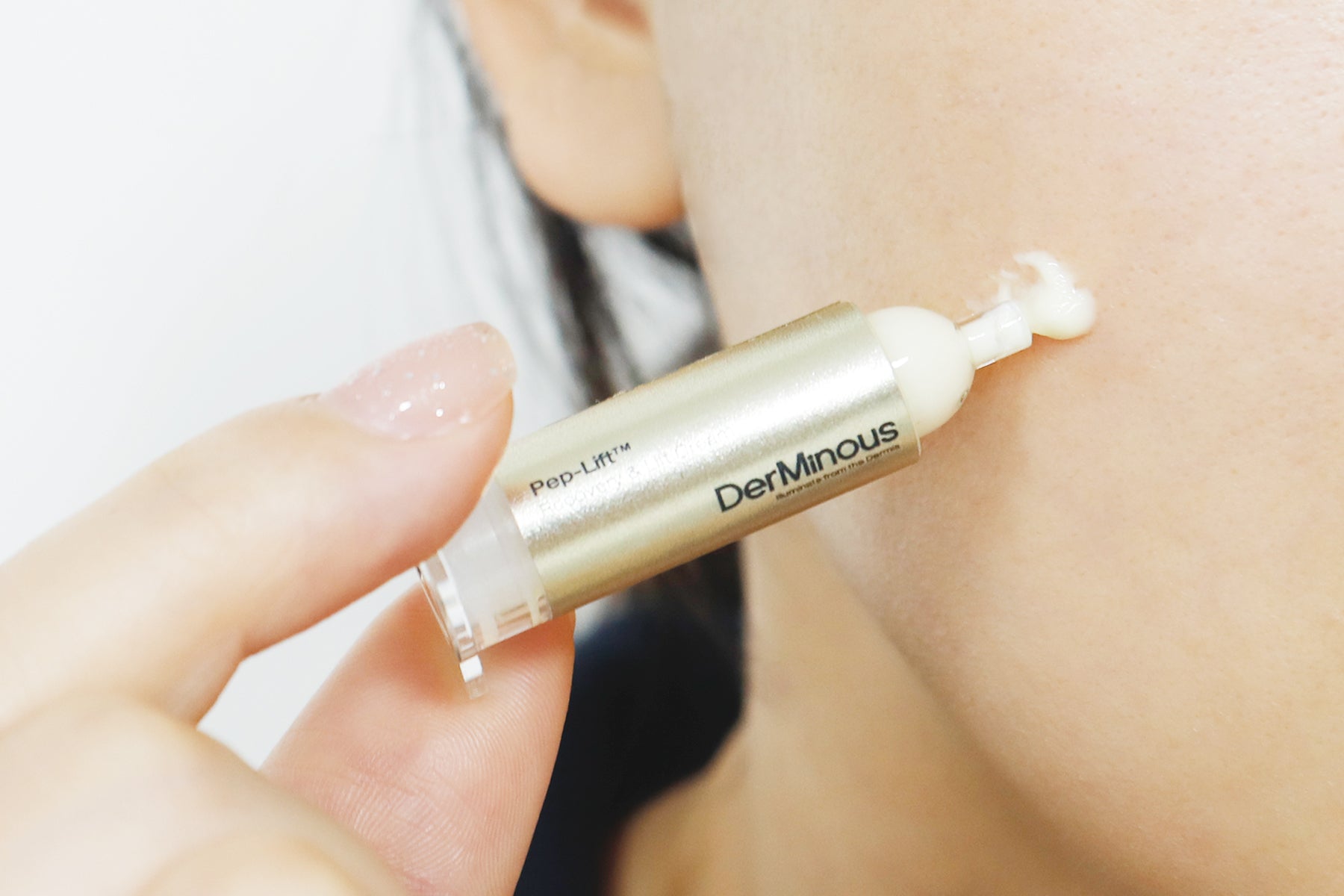
- Recovery & Lift Cream: Locks in actives with squalane, jojoba oil, and acetyl tetrapeptides to boost firmness over time.
This comprehensive approach ensures that brightening occurs within a context of barrier integrity and cellular rejuvenation—not at its expense. Unlike harsh exfoliants or high-dose acids that strip the skin, Derminous empowers the skin to heal itself from within.
Safety, Sustainability, and the Future of At-Home MedSpa
With rising demand for non-invasive, at-home aesthetic solutions—especially in North America and Europe—consumers are increasingly discerning about efficacy, safety, and scientific backing. Derminous meets this demand by merging biotech innovation (e.g., recombinant proteins, patented peptides) with user-centric design (single-use sterile devices, no alcohol or fragrance).
Moreover, the brand’s stance against needle reuse aligns with FDA and EU cosmetic safety guidelines, minimizing cross-contamination risks[9] . Each kit is designed for two monthly treatments, encouraging consistent yet non-excessive use—a balanced rhythm that supports sustainable skin health.
Conclusion: Brightening Reimagined
True radiance isn’t just about surface-level luminosity—it’s the glow of resilient, well-nourished, evenly toned skin. While niacinamide and vitamin C remain icons of brightening skincare, the future lies in how these ingredients are delivered and what they’re paired with. Derminous GeneLift™ exemplifies this evolution: replacing unstable vitamin C with advanced alternatives like tranexamic acid, enhancing penetration through gold micro-infusion, and wrapping the entire experience in a clinically inspired, barrier-supportive ritual.
For those seeking visible results without compromise, this system offers a compelling bridge between dermatology and daily self-care—proving that beauty, when rooted in science, is not only visible but enduring.
Footnotes
-
Niacinamide as a depigmenting agent. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jocd.12063↩
-
The role of niacinamide in skin barrier function. Dermatology and Therapy. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13555-019-00333-3↩
-
China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA). Patent ZL 2020116206743. http://epub.cnipa.gov.cn/↩
-
Topical vitamin C and the skin. Nutrients Journal. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5579659/↩
-
Tranexamic acid for melasma: mechanisms and clinical evidence. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40257-021-00637-2↩
-
Transdermal delivery challenges in cosmetics. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0378517319300121↩
-
Microneedling for enhanced drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0169409X18304495↩
-
Efficacy of microneedling in transdermal absorption. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. https://jddonline.com/articles/dermatology/S1545961618P0801X↩
-
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Guidance on Cosmetic Product Safety. https://www.fda.gov/cosmetics↩